Expertises
Our nuclear expertise in 6 areas
-
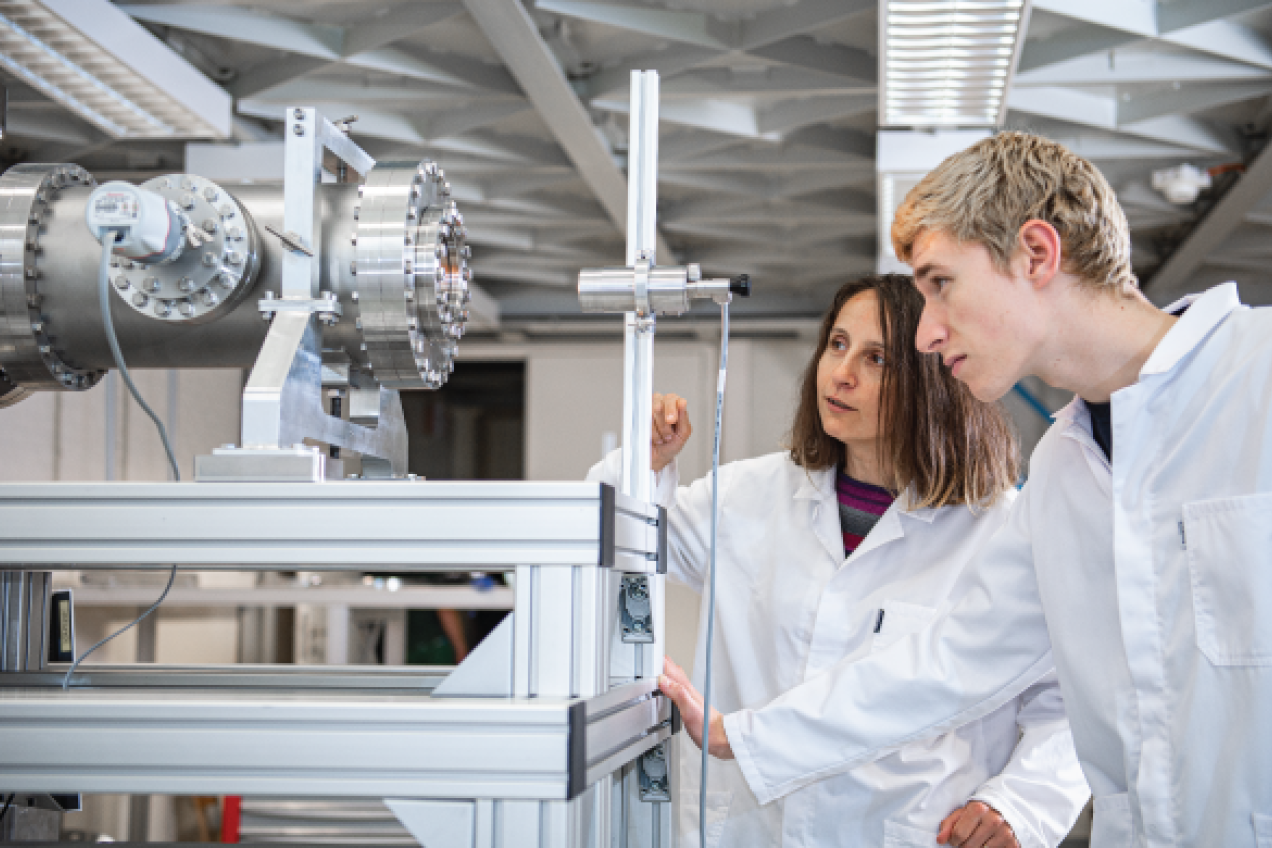

Exploring innovative nuclear systems
SCK CEN is, and remains, a pioneer by continuously improving knowledge and infrastructure. Find out how we are focusing on nuclear innovative systems, such as particle accelerators or new reactor technologies.
-
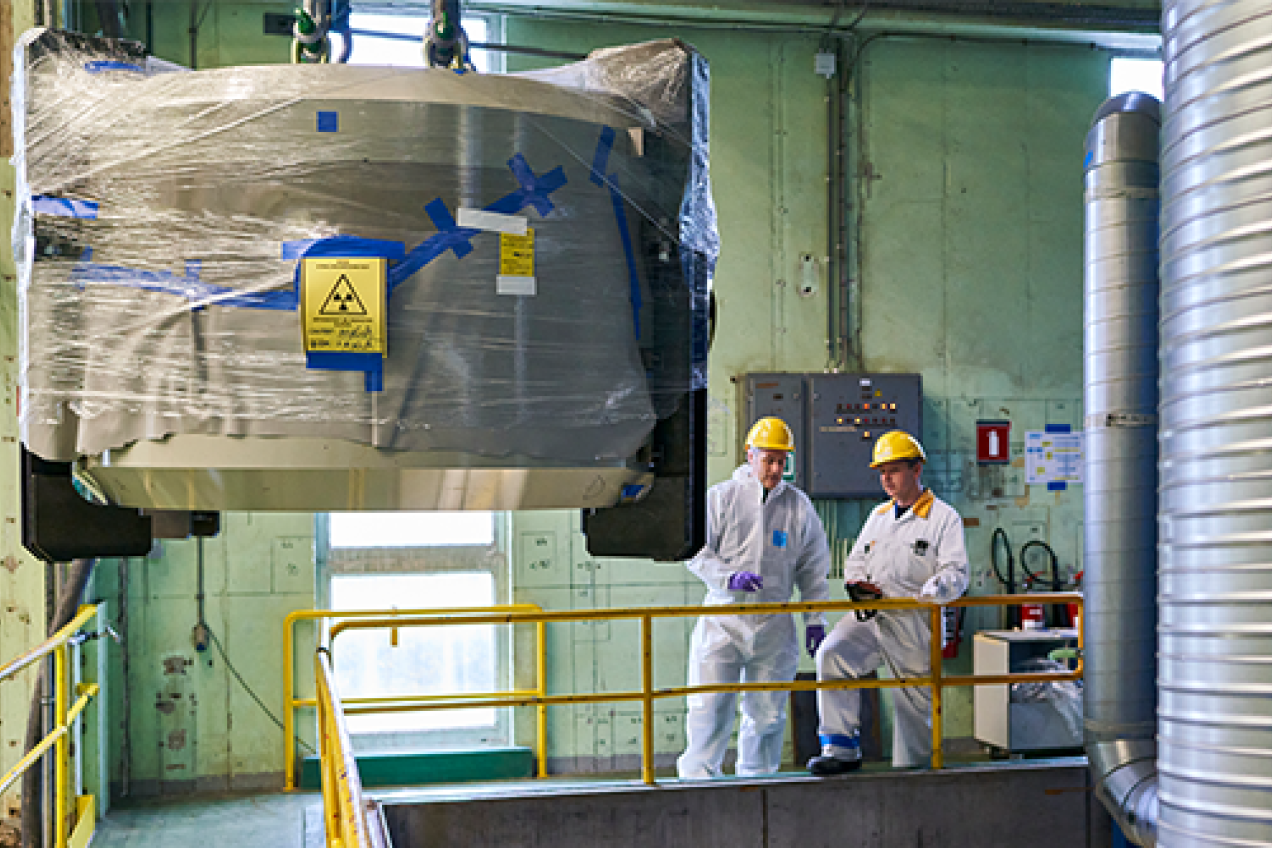

Exploring the nuclear lifecycle
By better managing radioactive waste streams, we protect people and the environment, and move one step closer to a better future. Learn more about how we dismantle nuclear facilities, restore contaminated sites and develop the best possible solutions for radioactive waste.
-
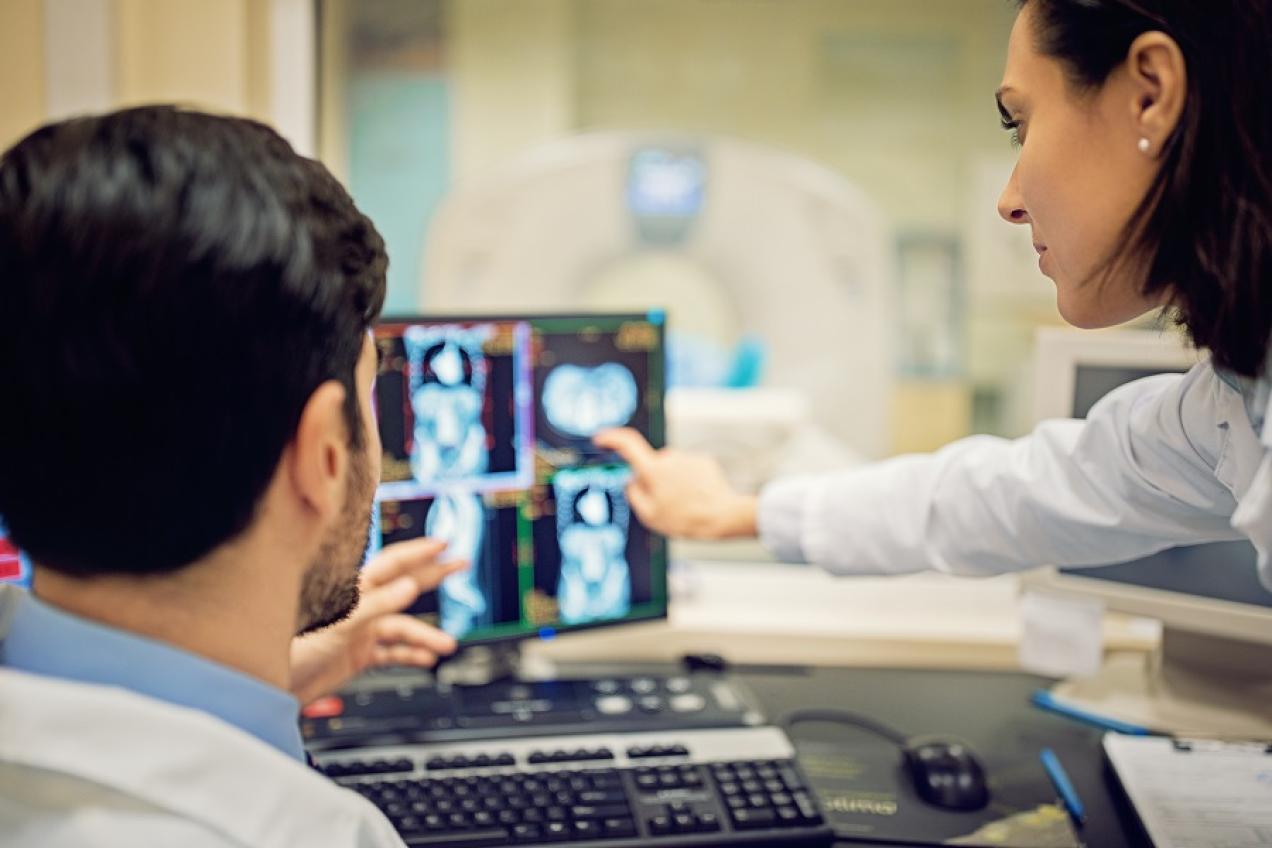
Exploring nuclear medicine
We are fighting cancer with cutting-edge research and the production of crucial medical radioisotopes. In this chapter you can read how we do this.
-
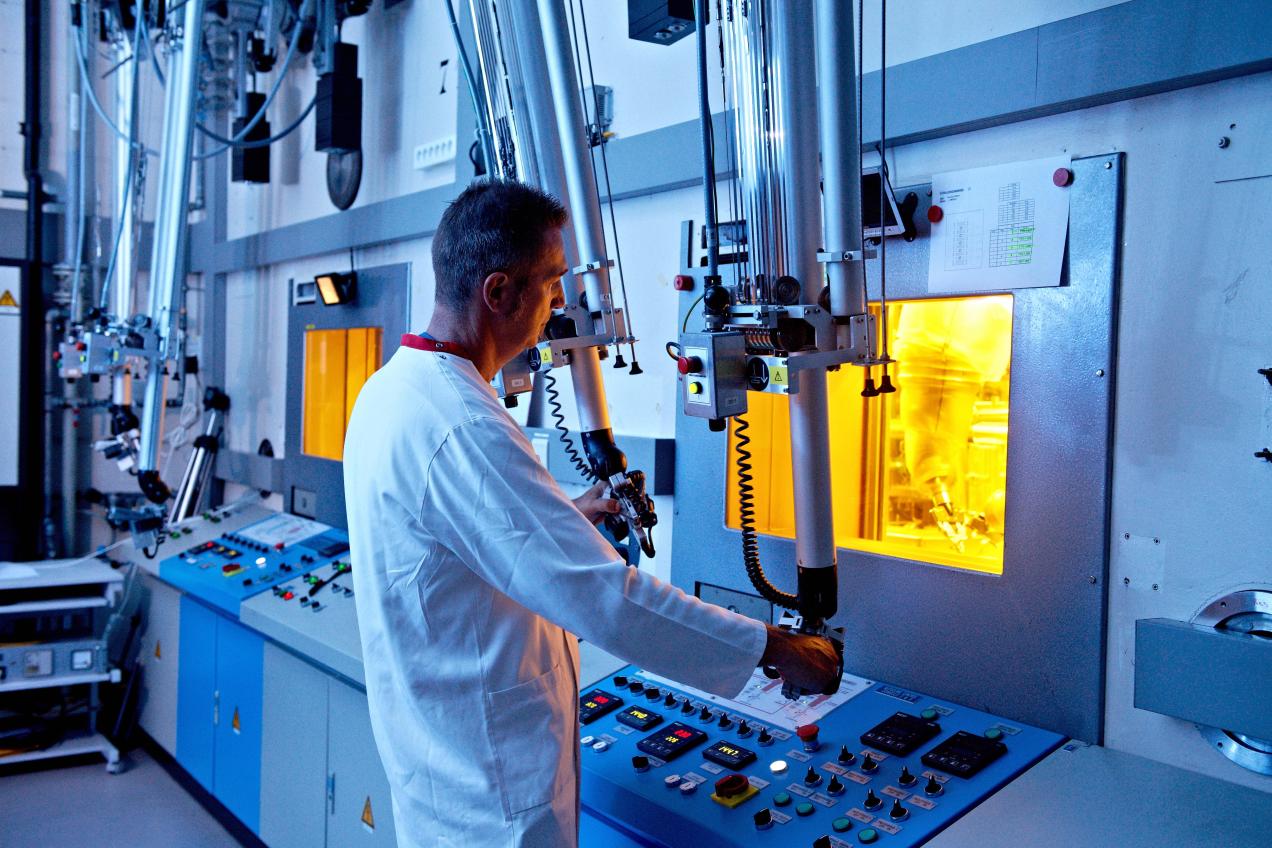

Guaranteeing nuclear safety
When you expose nuclear fuels or materials to intense radiation, you can see and measure the damage afterwards. In this way, SCK CEN analyses aging processes and thereby guarantees the safety of a nuclear reactor.
-
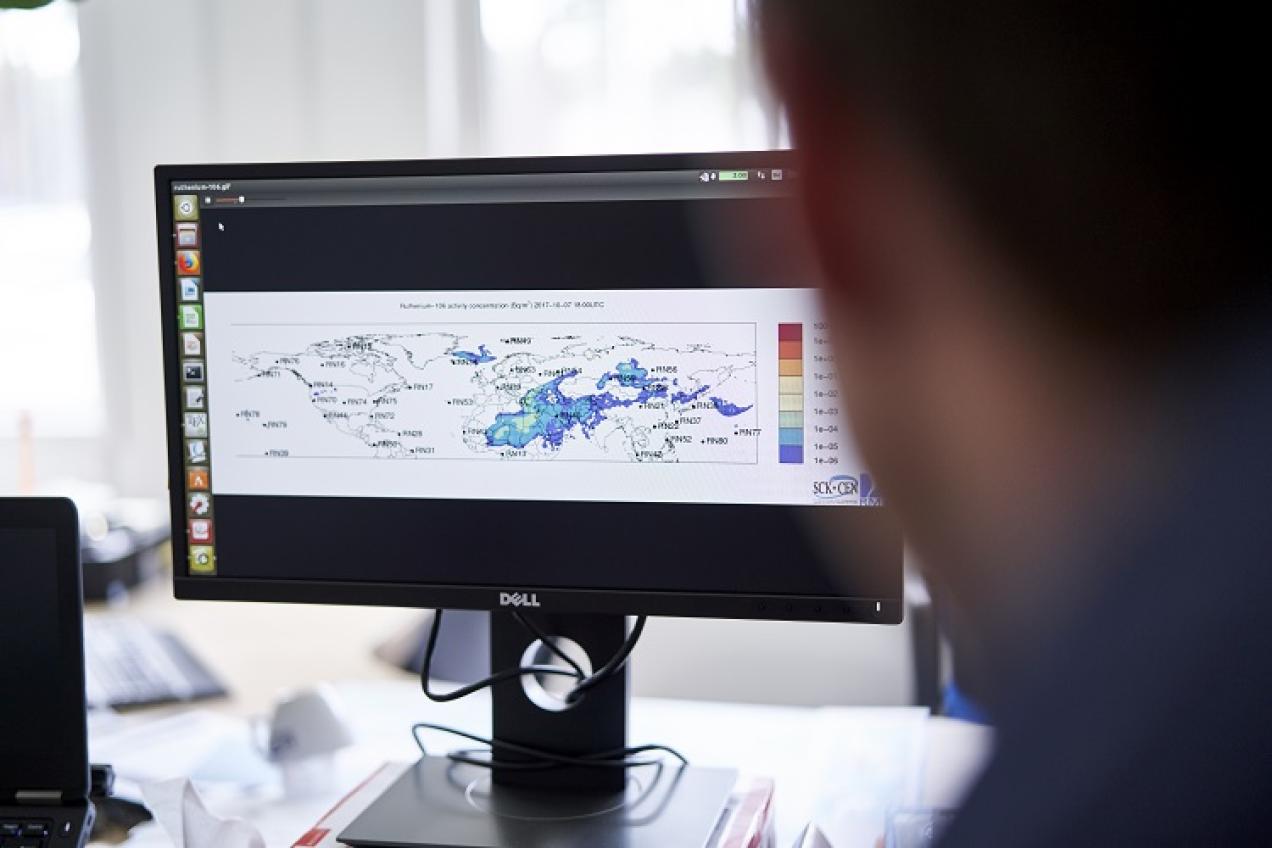

Guaranteeing radiation protection
You cannot see it, smell it, taste it or feel it, and yet radiation can have a major impact on our health. From measurements with drones to the close monitoring of astronauts, the protection of humans and the environment from ionising radiation is always our primary concern.
-

Guaranteeing nuclear knowledge
We strongly believe in the power of knowledge sharing. Find out here how we are building bridges between our society and the nuclear world.

Public institutional database of SCK CEN
SCK CEN collects, preserves and disseminates intellectual output through researchportal.sckcen.be. It provides access to peer-reviewed research articles, public reports, student theses and conference proceedings by SCK CEN staff and students.
✉️ For specific requests, please contact publications [at] sckcen [dot] be (publications[at]sckcen[dot]be).